What is Cloud Computing?
The term cloud refers to a network or the internet. It is a technology that uses remote servers on the internet to store, manage, and access data online rather than local drives. The data can be anything such as files, images, documents, audio, video, and more.
There are the following operations that we can do using cloud computing:
Developing new applications and services
Storage, backup, and recovery of data
Hosting blogs and websites
Delivery of software on demand
Analysis of data
Streaming videos and audio
Why Cloud Computing?
Small as well as large IT companies follow traditional methods to provide the IT infrastructure. That means for any IT company, we need a Server Room which is a basic need of IT companies.
In that server room, there should be a database server, mail server, networking, firewalls, routers, modem, switches, QPS (Query Per Second means how much queries or load will be handled by the server), configurable system, high net speed, and the maintenance engineers.
To establish such IT infrastructure, we need to spend lots of money. Cloud Computing comes into existence to overcome all these problems and reduce the IT infrastructure cost.
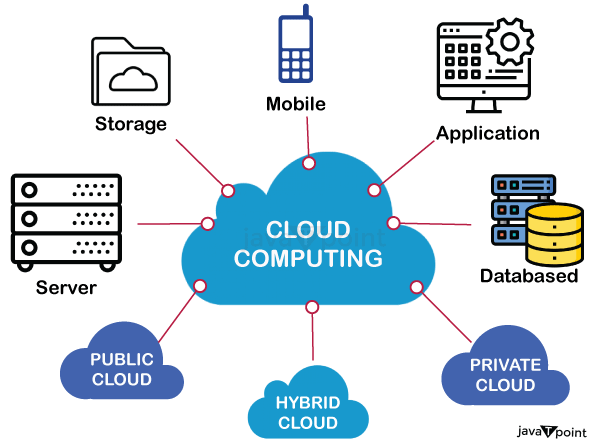
How does Cloud Computing works?
The cloud is basically a decentralized place to share information through satellite networks. Every cloud application has a host, and the hosting company is responsible for maintaining the massive data centers that provide the security, storage capacity, and computing power needed to maintain all of the information users send to the cloud.
"Cloud computing works by having companies host or maintain massive data centers that provide the security, storage capacity, and computing power to support cloud infrastructure. Clients pay for the rights to use their clouds along with an ecosystem to communicate between devices and programs."
These hosting companies can sell the rights to use their clouds and store data on their networks, while also offering the end user an ecosystem that can communicate between devices and programs (for example, download a song on your laptop and it’s instantly synced to the music app on your iPhone).
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
On-demand self-services: The Cloud computing services does not require any human administrators, user themselves are able to provision, monitor and manage computing resources as needed.
Broad network access: The Computing services are generally provided over standard networks and heterogeneous devices.
Rapid elasticity: The Computing services should have IT resources that are able to scale out and in quickly and on as needed basis. Whenever the user require services it is provided to him and it is scale out as soon as its requirement gets over.
Resource pooling: The IT resource (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) present are shared across multiple applications and occupant in an uncommitted manner. Multiple clients are provided service from a same physical resource.
Measured service: The resource utilization is tracked for each application and occupant, it will provide both the user and the resource provider with an account of what has been used. This is done for various reasons like monitoring billing and effective use of resource.
Multi-tenancy: Cloud computing providers can support multiple tenants (users or organizations) on a single set of shared resources.
Virtualization: Cloud computing providers use virtualization technology to abstract underlying hardware resources and present them as logical resources to users.
Resilient computing: Cloud computing services are typically designed with redundancy and fault tolerance in mind, which ensures high availability and reliability.
Flexible pricing models: Cloud providers offer a variety of pricing models, including pay-per-use, subscription-based, and spot pricing, allowing users to choose the option that best suits their needs.
Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect their users’ data and ensure the privacy of sensitive information.
Automation: Cloud computing services are often highly automated, allowing users to deploy and manage resources with minimal manual intervention.
Sustainability: Cloud providers are increasingly focused on sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient data centers and the use of renewable energy sources, to reduce their environmental impact.

Advantages of Cloud Computing
As we all know that Cloud computing is trending technology. Almost every company switched their services on the cloud to rise the company growth.
Here, we are going to discuss some important advantages of Cloud Computing-
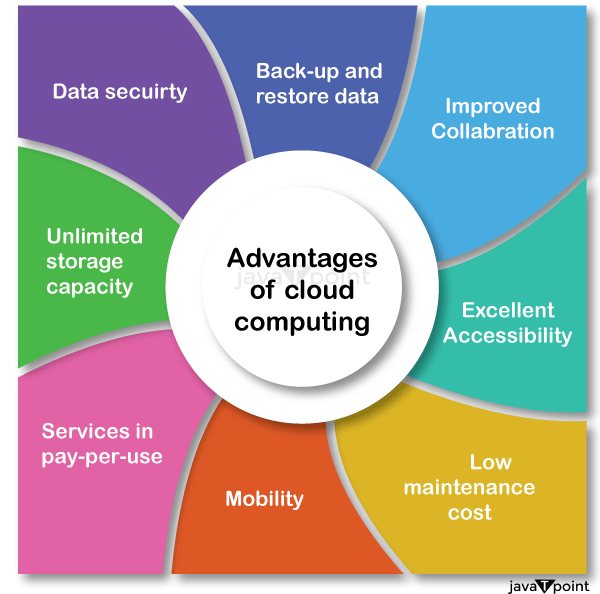
1) Back up and restore data
Once the data is stored in the cloud, it is easier to get back up and restore that data using the cloud.
2) Improved collaboration
Cloud applications improve collaboration by allowing groups of people to quickly and easily share information in the cloud via shared storage.
3) Excellent accessibility
The cloud allows us to quickly and easily access and store information anywhere, anytime in the whole world, using an internet connection. An internet cloud infrastructure increases organization productivity and efficiency by ensuring that our data is always accessible.
4) Low maintenance cost
Cloud computing reduces both hardware and software maintenance costs for organizations.
5) Mobility
Cloud computing allows us to easily access all cloud data via mobile.
6) Services in the pay-per-use model
Cloud computing offers Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to the users for accessing services on the cloud and pays the charges as per the usage of the service.
7) Unlimited storage capacity
Cloud offers us a huge amount of storage capacity for storing our important data such as documents, images, audio, video, etc. in one place.
8) Data security
Data security is one of the biggest advantages of cloud computing. The cloud offers many advanced features related to security and ensures that data is securely stored and handled.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a disruptive technology that offers businesses several benefits like scalability, flexibility to set up and manage their IT infrastructure, and pay-as-you-use models. However, there are also several disadvantages of cloud computing that pose challenges to businesses. These include:
1) Downtime
Businesses receive cloud computing services only through the Internet. When there is an internet outage or weak connectivity, services get interrupted and this increases downtime. Therefore, one of the major criticisms of cloud computing is its high dependency on the Internet.
2) Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy threats are other disadvantages of cloud computing. According to a survey, nearly 98% of companies using cloud computing services experienced at least one data breach from 2020 to 2022. Inadequate cloud security measures lead to data leakage over cloud networks which can result in intellectual property theft, contract breaches, and malware attacks. Hackers can also control how companies provide services to their customers or end-users. This leads to a loss of business opportunities and a decrease in revenue.
3) Vulnerability to Attacks
Private clouds are considered the most secure for businesses in terms of data security. However, the cost of setting up private clouds is higher in comparison to public, hybrid, and multi-clouds. Therefore, many businesses prefer public, hybrid, and multi-cloud computing services. As these clouds provide services to multiple users over the same network, businesses become vulnerable to cyber attacks which can lead to data loss or data leakage.
4) Limited Control and Flexibility
In public, hybrid, and community clouds, all cloud computing services are completely managed by cloud service providers. This offers limited control and flexibility to customers, restricting their access to various services and applications. Therefore, many companies enter into separate end-user license agreements to gain control of the cloud’s services and applications.
5) Vendor Lock-in
Vendor lock-in refers to a situation where companies using cloud computing services of a particular vendor are unable to switch to a different vendor. This usually happens because of high switching costs, large amounts of data which is difficult to migrate, and several other complexities. In case of vendor lock-in, companies are forced to receive services from a particular vendor. This affects their operational workflow and efficiency.
6) Cost Concerns
Costs are both a significant advantage and disadvantage of cloud computing. While it helps small businesses avail quality services without investing large amounts to set up IT infrastructure, it can also increase expenditure for companies as there are several hidden costs involved which emerge at a later stage. These include data transfer, cloud utilization, and data migration costs.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be categorized in two ways:
Deployment Models
Service Models

1. Deployment Models
Based on how it is located, cloud computing can be classified in the following three ways:
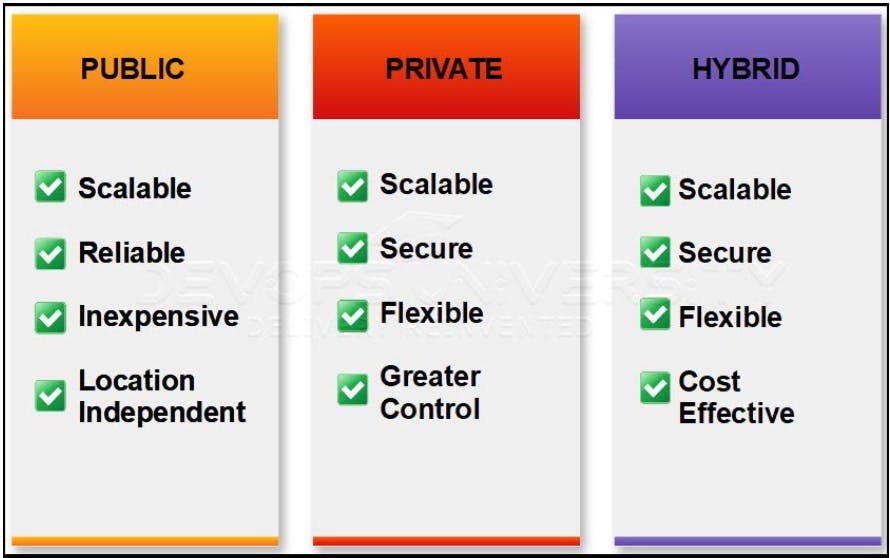
Public cloud
A cloud platform based on the standard cloud computing model in which vendors offer resources and application storage to consumers over the internet is called public cloud computing. The hardware resources in the public cloud are shared among multiple users and are accessible over a public network. Startups having budget constraints, or organizations where high security is not a priority opt for Public Cloud Computing to save money. Here, the computing infrastructure is hosted by the cloud vendor at the vendor’s premises. The customer has no visibility and control over the location of the host computing infrastructure.
Advantages
It offers greater scalability
Its cost-effectiveness helps you save money.
It is reliable as no single point of failure will interrupt your services.
SaaS, Paas, Iaas are available on the Public Cloud platforms easily
No dependency on location
Disadvantages
No control over privacy or security
Not apt for applications handling sensitive data
Lacks flexibility as the platform depends on the vendor
No strict data management protocols
Private Cloud
A secure cloud environment where the computing infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization only and not shared with other organizations. The additional security allows companies to keep confidential and sensitive data in the private cloud environment.
Private clouds are of two types:
On-premise private clouds
Externally hosted private clouds
Externally hosted private clouds are exclusively used by a single organization, but are hosted by a third-party cloud provider. They are cheaper than On-premise private clouds.
Advantages
Greater Security and Privacy
Greater control over system configuration according to the company’s need
Reliable performance
Enhanced quality of service
Cost-effective
Disadvantages
Expensive compared to the public cloud
Requires IT Expertise
Hybrid Cloud
In this computing model, a combination of both public and private clouds is used. In this model, companies can use the public cloud for non-confidential data transfer and switch to the private cloud for sensitive data transfer or hosting of critical applications.
This helps companies achieve maximum efficiency and deliver better results to clients.
It is gaining popularity in many businesses, as it gives the benefits of both models.
Advantages
It is scalable
It is cost-efficien
Offers better security
Offers greater flexibility
Disadvantages
Infrastructure Dependency
Possibility of security breach through public cloud
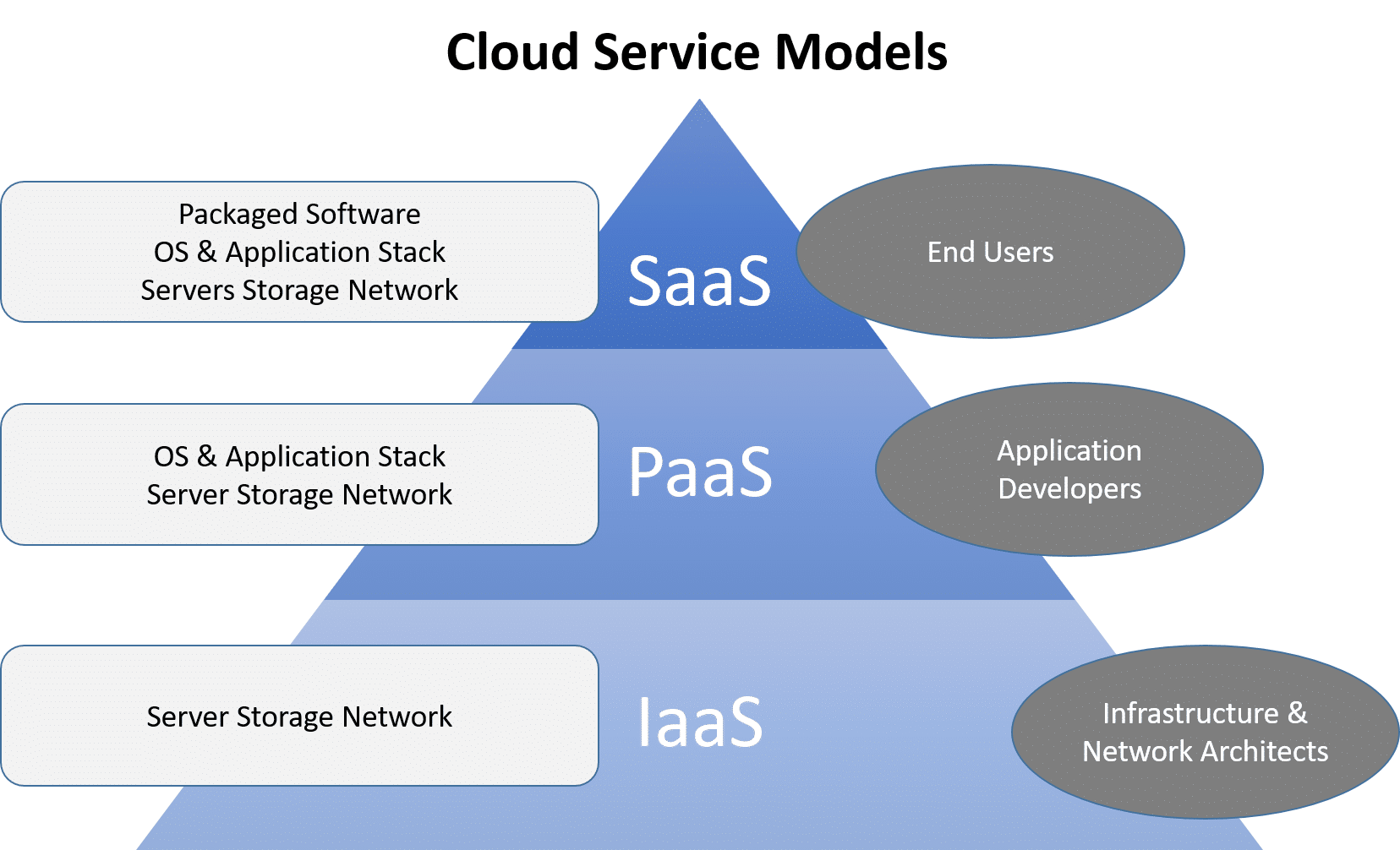
2. Service Models
Based on the services offered, clouds are classified in the following 3 ways:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
offers hardware-related services through cloud computing. These include storage services (database or disk storage) or virtual servers.
It provides access to primary resources like physical machines, virtual machines, virtual storage, IP addresses, VLANs etc.
All of the resources,s mentioned above are available to the end users through server virtualization. Customers access these resources as if they own them.Characteristics
Automated administrative tasks
Dynamic scaling
Platform virtualization
Internet connectivity
Benefits
Users with admin rights on VMs have full control over computing resources
Flexible and efficient renting of computer hardware
Portable and interoperable with legacy applications
Issues
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS have common issues like network dependency and browser-based risks. IaaS also has some specific issues, like:
Compatibility with legacy security vulnerabilities
Virtual Machine sprawl
Robustness of VM-level isolation
Data erase practices
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
offers the runtime environment for applications. It also offers the tools required for the development and deployment of applications. PaaS has a point-and-click tool feature that enables even non-developers to create web applications. Some of the major PaaS providers are Google’s Application Engine, Microsoft’s Azure, Salesforce.com’s force.com. Developers may log on to these websites and use the built-in API to create web-based applications.
Characteristics
Browser-based development environment.
Built-in security, scalability and web service interfaces.
Workflow, approval processes, and business rules.
Easy integration with other applications on the same platform.
Benefits
Lower administrative overhead
Lesser ownership cost
Scalable solutions
More current system software
Issues
Significant burdens on customer’s browsers to maintain
connections to the provider’s machines
Lack of portability between PaaS clouds
Event-based processor scheduling
Security engineering of PaaS applications
Software-as–a-Service (SaaS)
the model provides software applications as a service to the users. It refers to software that is deployed on a hosting service and is accessible through the Internet. Software as a service (SaaS) includes a complete software offering on the cloud. Users can access a software application hosted by the cloud vendor on a pay-per-use basis. The first in this field was Salesforce.coms online Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and some other examples include Google’s Gmail and Microsoft’s Hotmail, Google Docs, and Microsoft’s online version of office.
There are several SaaS applications listed below:
Billing and invoicing systems
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications
Help desk applications
Human Resource (HR) solutions
Some of the SaaS applications are not customizable like Microsoft Office Suite, but SaaS provides Application Programming Interface (API), which the developers use to customize an application.
Characteristics
SaaS makes the software available over the Internet.
The software applications are supported by the vendor.
The license to the software may be subscription-based or usage-based
Billing is regular.
SaaS applications are cost-effective as there is zero maintenance at the user end.
Available on demand.
Scalable on demand.
Automatic updates.
SaaS offers a shared data model where multiple users can share a single infrastructure instance.
All users run the same version of the software.
Benefits
Using SaaS is beneficial in terms of scalability, efficiency and performance.
Some of the benefits are:
Modest software tools
Efficient use of software licenses
Centralized management and data
Platform responsibilities managed by the provider
Multi-Tenant solutions
Issues
Browser based risks
Network dependence
Lack of portability between SaaS clouds
Open SaaS and SOA(Service-oriented architecture)
Open SaaS uses SaaS applications, which are developed using open source programming language. These SaaS applications can run on any open source operating system and database. Open SaaS has several benefits listed below:
No License Required
Low Deployment Cost
Less Vendor Lock-in
More portable applications
More Robust Solution
Cloud Service Providers in market
1) Google Cloud Platform
GCP uses resources located at Google data centers.
GCP is an integrated storage for live data, used by developers and enterprises.
Apart from the free trial, GCP offers various flexible Pay-As-You-Go payment plans.

2) Microsoft Azure
It is used for deploying, designing, and managing applications through a worldwide network.
Was known as Windows Azure, previously.
Supports various operating systems, databases, tools, programming languages, frameworks, etc.
A free trial for 30 days is available.

3) Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is the safest cloud service platform offering a wide range of infrastructure services like database storage, computing power, networking, etc.
By using AWS, Users are able to build scalable, complicated, and flexible applications, using AWS.
One can experience AWS and do hands-on using free-tier services.
4) IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud offers all cloud delivery services – Iaas, PaaS, and SaaS.
IBM Cloud gives the freedom to the users to choose and combine the desired tools, data models, and delivery models in designing and creating next-generation services or applications.
IBM Cloud is used to build pioneering way-outs that can gain value for your business and industry.
5) Red Hat
It is an Open Cloud technology that provides agile and flexible solutions to IT companies.
We can modernize, update and manage the applications from a single point and integrate all the desired aspects into a single solution, using Red Hat Cloud.
Red Hat Cloud Infrastructure helps us in building and managing a cost-effective, open cum private cloud.
6) Salesforce
Salesforce Cloud Computing offers all the business applications like CRM, ERP, customer service, sales, mobile applications, etc.
Salesforce cloud computing comprises multiple cloud services like Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud, etc.
Salesforce Sales Cloud helps in managing the customer’s contact information and automating the business processes etc.
7) Oracle Cloud
Oracle Cloud is available as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
Oracle Cloud helps organizations in transforming their business and reducing IT Complexity.
Oracle Cloud SaaS is a completely data-driven and secure cloud environment.
Oracle Cloud PaaS aids IT Enterprises and individual developers to develop, connect, protect, and share data across applications.
Oracle Cloud IaaS is a wide set of subscription-based, integrated services.
8) SAP
SAP Cloud Platform is an enterprise service with a wide range of application development services.
SAP has powerful business networks, cloud collaboration, and advanced IT security, and hence it is considered the best cloud provider.
SAP has a universal foundation named SAP HANA, for its cloud services.
SAP Cloud Platform is modernizing the way enterprises work on iPhones and iPad.
9) Vmware
It is a universal leader in virtualization and Cloud Infrastructure.
VMware vCloud Air is a safe and protected public cloud platform offering networking, storage, disaster recovery, and computing, etc.
VMware’s Cloud solutions help organizations maximize their cloud computing profits by combining the services, technologies, and guidance needed to operate and manage the staff, etc.
Top most famous international certification on Cloud Computing
1) Amazon Web Services (AWS) Solutions Architect - Associate
The AWS Solutions Architect - Associate certification involves a multiple-choice exam that tests your ability to deploy, manage, and use various services in AWS, the leading platform in the cloud market. The certification shows your proficiency in the basic technical concepts of AWS cloud engineering that can position you to qualify for related jobs.
Just starting out with AWS? The AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certification is designed for candidates with a few months of experience and can be a way to build up experience for the AWS Solutions Architect - Associate certification.
Cost: $150
What’s being tested: Compute, networking, storage, and database AWS services; deployment and management; basic architectural principles of building in AWS; global AWS infrastructure; network technologies in relation in AWS; among other subjects

2) Microsoft Certified: Azure Fundamentals
With the second largest market share in the cloud space, Azure can be a useful cloud platform to learn. The foundational certification for Azure involves the AZ-900 exam and is designed for those with both technical and non-technical backgrounds. It’s a solid certification to get you up to speed with fundamental Azure knowledge. From there, you can go on to get the Azure Administrator Associate or Azure Developer Associate certifications, though it’s not a prerequisite.
Cost: $99
What’s being tested: The differences between cloud services like IaaS and PaaS; benefits of using cloud services; core Azure services like virtual machines (VMs), containers, Kubernetes, and database services; understanding of Azure core solutions and management tools; basic security, include network security; and other subjects

3) Google Associate Cloud Engineer
Getting certified as a Google Associate Cloud Engineer will mean showing competency in the basic aspects of working with Google Cloud. This includes setting up a cloud solution environment, managing storage and databases, and configuring access and security, among other things.
Cost: $125
What’s being tested: Setting up cloud solutions by creating projects, managing users in Cloud Identity, and managing billing configuration; planning and configuring compute resources, data storage options, and network resources; deploying Google Kubernetes Engine, applications; managing a virtual machine (VM); and more
4) IBM Certified Technical Advocate - Cloud v3
IBM cloud services take up less market share than the others, but can still be useful in industries that use IBM cloud platforms. The IBM Certified Technical Advocate - Cloud v3 (formerly known as IBM Certified Solution Advisor) is the foundational certification for IBM cloud. If you work at a place that primarily designs solutions based on the IBM cloud, or hopes to do so in the future, this certification can make sense. There are several more advanced levels of IBM cloud certifications, like the IBM Certified Professional Architect - Cloud v5.
Cost: $200
What’s being tested: Understanding of cloud concepts; IBM Cloud components; architectural principles and patterns; networking and security; Cloud Native practices cloud deployment; among other things
5) Cloud Security Alliance: Certificate of Cloud Security Knowledge (CCSK)
The CCSK is issued by the Cloud Security Alliance, a vendor-neutral certification provider. This means that the things you learn from getting a certification can be applied to different cloud platforms. The CCSK focuses on the fundamentals of cloud security. There are other advanced certifications, like the CCSP from (ISC)2, that indicate a professional level of mastery of cloud security.
Cost: $395
What’s being tested: Cloud computing concepts and architecture; governance and enterprise risk management; legal issues and contracts; data security; virtualization and containers; and more
That’s all for today. Thank you
Follow me on:
facebook.com/parthokumar.saha.39

